Have you ever searched for Free Wifi Near Me, Free wifi near me without Password? I guess yes! The term Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, and they are used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing close internet-enabled devices to transmit and exchange data through radio waves.
For hackers to eavesdrop or intercept network traffic, all they need is to find a close wifi access point. This means that poorly configured access point encryption or services that allow data to be sent without any encryption could become a security threat as users’ data can be collected without their knowledge.
Related: Funny WIFI Names – Meaning & List of 50 Funny WIFI Names
Also read: How to Find Router IP Address
Unaware? Risk of Using Free Wifi Near Me
The case of public Wi-Fi network usage could also create a data leak as traffics are not always encrypted, as such, hackers can take advantage of it.
The Kaspersky survey stated that 70% of tablet owners and 53% of smartphone / mobile phone owners use public Wi-Fi hotspots. However, because data sent through public Wi-Fi can easily be intercepted, many mobile devices and laptop users are at security risk of their private data.
This suggests that you must ensure the encryption of traffic at your wireless access points in order to protect your private data.
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) statistics also revealed how the situation varies from country to country.
They compared the situation with Wi-Fi traffic encryption in different countries using data from their threat database. They counted the number of reliable and unreliable networks in each country that has more than 10 thousand access points known to them (this excludes Antarctica and other regions where there is not enough data to draw any conclusions).
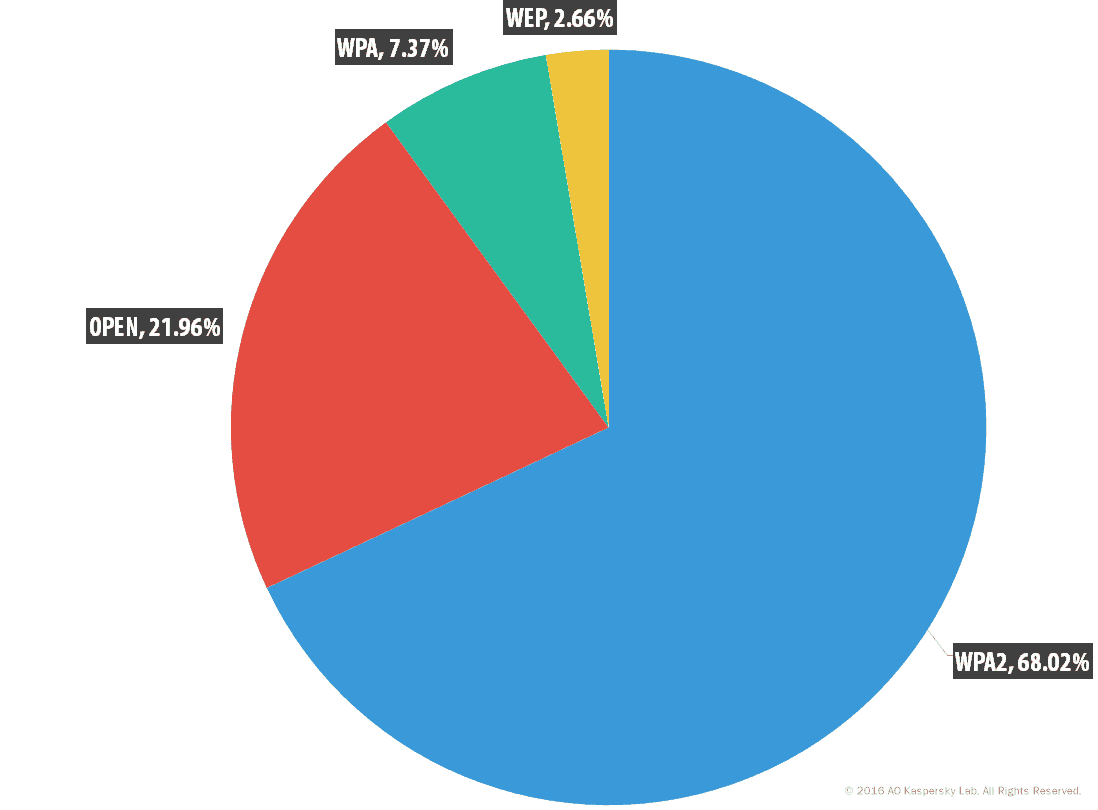
In the KSN analysis of data across the world for almost 32 million Wi-Fi hotspots accessed by the wireless adapters of KSN users by comparison can be seen in the image below.
Also check: Top Affiliate Programs you can join and Start Earning
“Approximately 24.7% of Wi-Fi hotspots in the world do not use any encryption at all. This basically means that by using an antenna capable of sending and receiving data at 2.4 GHz, any individual located near an access point can easily intercept and store all user traffic and then browse it for data they are interested in.
“The WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) protocol for encryption of data transferred over Wi-Fi is used by approximately 3.1% of all analyzed access points. The protocol was the first to be created, quite a long time ago, and is now completely unreliable – it would take hackers just a few minutes to crack it.
“Around three-quarters of all access points use encryption based on the Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) protocol family. The protocols from this family are currently the most secure. The effort required to hack WPA depends on its settings, including the complexity of the password set by the hotspot owner.
“Overall, it can be said that today’s WPA/WPA2 “non-enterprise” versions are reasonably, but not absolutely, secure. In particular, they allow brute-force and dictionary attacks. There are ready-to-use publicly available tools (aircrack-ng and similar software) for performing such attacks, as well as a large number of manuals.
Below are the dangers of using free public WiFi and what you must do to ensure safety.
Also Read: 10 Signs of a Malware Infection on your Computer
Suggested read: A Comparative Analysis of CyberGhost VPN, Avast VPN, and NordVPN
What Are the Dangers of Using Free Wifi Near Me?
6 Dangers of Using Free Public WiFi
1. Harvest Personal Data
Do you ever wonder why data protection is taken seriously? Data has become a billion-dollar industry. In fact, the study from Globenewswire estimated the market size of data at $240.56 billion in 2021 and $271.83 billion in 2022. The increasing data generation from Facebook, Snapchat, WhatsApp, Instagram, and other such platforms results in huge databases.

And this is why you must protect your data such as personal data, Login details, identity information, financial data, and so on. Most Hackers are in the comfort of their homes sniffing around and looking for loopholes to exploit, and your data can be collected using free public WiFi if you are not very careful. You sure know what could happen when someone gets access to your banking details!
Suggested read: Pegasus Spyware – The Most Intelligent Spyware Ever Built
Also read: How to know and What to do if your Phone is Being Monitored by Spyware
2. Malware Distribution
Malware is an application or software intentionally engineered to cause disruption to a computer, smartphone, server, client, or computer network, leak private information, gain unauthorized access to information or systems, deprive access to information, or unknowingly interfere with the user’s computer security and privacy.
Malware can be distributed to personal computers or internet enable gadgets in form of worms, ransomware, viruses, and trojan horse with the sole purpose of harvesting your data. This can also be passed around from an unencrypted public WiFi. A person or wifi owner with bad intentions can plant malware on your device if you are on the same Wifi and this can be used against you.
This can be possible by using the WiFi network to place ads on every website you access on your device. While the website itself does not run ads, the WiFi however can be engineered to overlay the malware over other websites. This means that you will experience the ads overlay or pop-up sometimes when you are on that Wifi network that has been engineered with malware.
Also read: Internet Security Threats to Watch for
Read also: Complete Guide to Virtual Private Server (VPS)
Read also: What is a Virtual IP Address – Purpose and Benefits
3. Packet Sniffing
Packet sniffing is the process of using a packet sniffer or network analyzer (a computer program such as a packet capture appliance) to intercept and log traffic that passes over a computer network or part of a network. It is the act of gathering, collecting, and monitoring data that pass through a computer network or the internet.
[ads1]
It means every packet that travels across the internet or a local network is gathered for a wide range of purposes such as – monitoring the traffic & bandwidth, maintaining networks, analyzing the data collected by the device, and so on. It is often used for various purposes by hackers, ISPs, security administrators, and so on.
However, black hat hackers can take advantage of packet sniffing. A hacker or someone with bad intentions on the same WiFi network (unencrypted) can eavesdrop on data going through your network by using a packet sniffer.
Also Read: 10 Signs of a Malware Infection on your Computer
4. Businesses Cyber Attack
It was in the year 2014 when the four worst data breaches that compromised government data occurred. The hacking of big companies like eBay, SONY, JPMorgan Chase, and Home Depot in fact made headlines on Forbes as top 5 most brutal cyber-attacks. So, it has not always been just businesses or business owners. Today, small businesses are mostly targeted by hackers.
You must also note that this type of attack can come in the form of a password attack, viruses, phishing attack, spyware, cross-site scripting, keylogger, and so on.
Let’s paint a scenario. You are a business owner; you went on a trip and there you found free public WiFi! You connected and started surfing the net without thinking about the potential risk. This is not a good practice for business owners or anyone. You go to a public space, there you see free WiFi and you are connected to one. While some are opened with good intentions, however, some are also opened with bad intent and you should be careful.
Also read: How to Choose a Good Web Hosting for your Website or Business
Suggested read: Social Engineering and Prevention Measures
Related: 14 Types of Hackers and How to Prevent Hacking
5. Man-In-The-Middle Attacks
A man-in-the-middle (MITM) is a cyberattack where the attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communications between two parties who believe that they are directly communicating with each other, as the attacker has inserted themselves between the two parties.
One example of a MITM attack is active eavesdropping, in which the attacker makes independent connections with the victims and relays messages between them to make them believe they are talking directly to each other over a private connection, when in fact the entire conversation is controlled by the attacker.
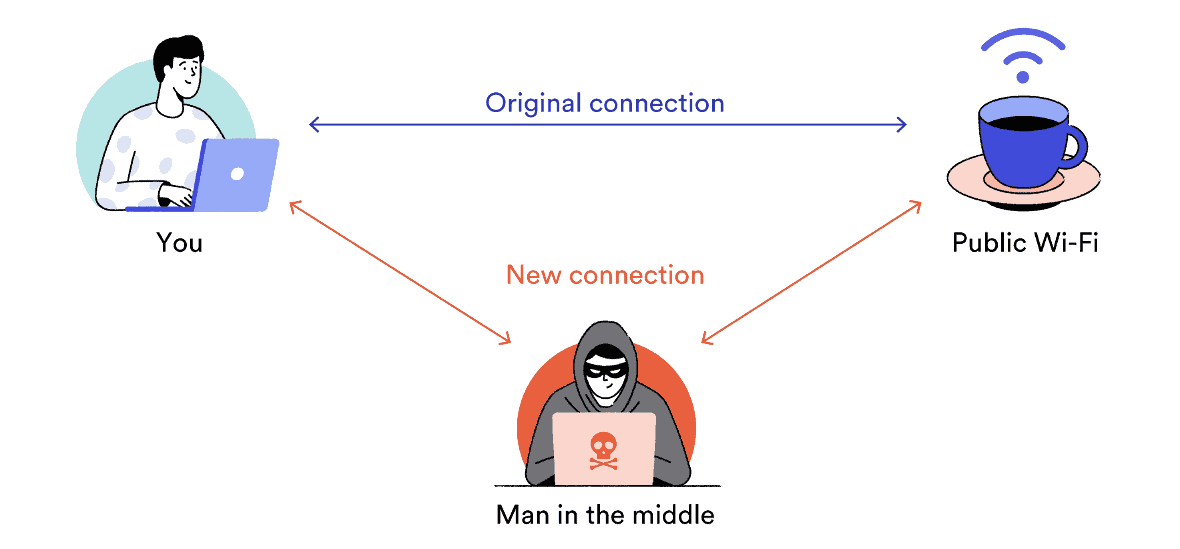
A man-in-the-middle can penetrate a secure public Wifi to trick you into joining his own network. An example; You are staying in an Airbnb/hotel for a period. you get access to the hotel WiFi which has a secure wifi network with the name “Goodpeople hotel”. You need access to the internet while there and you connect to the open Wifi with the name “Gooodpeople hotel”. Now, there is a misspelling in the WiFi name and if you don’t pay attention, you might miss the spelling difference which then opens you to possible penetration.
While “Goodpeople hotel” is the actual hotel’s wifi, the replicate (Gooodpeople hotel) with a misspelling of triple O could be a public WiFi nearby opened by another person for the purpose of impersonation.
This means that when you connect to such network, all data going through your connection would go through the hacker’s computer. Hence, the man-in-the-middle is a potential threat to your data.
Also Read: 9 Most Deadliest Computer Viruses that Stood the Test of Time
6. Unsecured Connections
The term unsecured connection also means an unencrypted connection. An unsecured connection means your Wi-Fi connection is unprotected and may create data leaks.
Using an unsecured website is also dangerous and your data can be collected from websites that are not protected by an SSL certificate if you submit any information there.
When you access a website that supports encryption, the data going through the website is protected using a secure key. This means a hacker or someone with bad intent can not intercept the connection without a key. The image below demonstrates what a secure and unsecured website looks like.

SSL is popularly known as Secure Sockets Layer and it is a security layer that creates an encrypted link between a web server and a web browser. SSL Certificates are small data files that digitally bind a cryptographic key to an organization’s details. When installed on a web server, it activates the security padlock and the HTTPS protocol provides secure connections from a web server to a browser.
Also read: 6 Password Safety Tips you Should Never Ignore
Public WiFi Usage Security Tips to Ensure Safety
In a case where you have no option but to use free public WiFi, the following are the best practices for protecting yourself from the danger of public Wifi;
1. Keep your Security data as Safe as Possible
The first step you should take in order to prevent data leaks is to keep your security information private and as safe as possible. And never share it with anyone unless it is someone you really trust.
Firstly, if you have to connect to a public WiFi network with no protection measures in place, then you must ensure not to share any private information or access any sensitive websites. Don’t use public wifi to access your internet banking or read important emails. This practice will limit your risk of being exposed.
2. Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN is a virtual private network that allows you to mask IP, send, and receive across a public or shared network. It allows you to access the internet anonymously while preventing data leaks.
A VPN allows you to stay invincible while you send and receive data over a WiFi network. Below are recommended VPN providers you can use;
We Recommend: Best Virtual Private Network Providers
Cover your internet tracks. Below are the VPNs we recommend for your internet protection
| Best VPNs | Categories | Websites |
|---|---|---|
| VPN/Internet Security | https://www.securi.net/ | |
| VPN/Internet Security | https://www.cyberghost.com/ | |
| VPN/Internet Security | https://privadovpn.com/ | |
| VPN/Internet Security | https://atlasvpn.com/ | |
| VPN/Internet Security | https://www.avast.com/ | |
| VPN/Internet Security | https://www.ipvanish.com/ | |
| VPN/Internet Security | https://www.avg.com/ | |
| VPN/Internet Security | https://nordvpn.com/ | |
| VPN/Internet Security | https://www.expressvpn.com/ |
