In this article, I cover DNS Resolution Error 1001 and Other Common DNS Issues and what you should know. What happens when DNS fails?
When DNS fails, users may encounter various errors, including the DNS Resolution Error 1001. The Domain Name System (DNS) is a fundamental component of internet infrastructure that translate human-readable domain names into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network.
Read also: 4 Basic Types of IP Address
What is the Importance of DNS?
DNS functions as the internet’s phonebook that enables users to access websites using domain names instead of numerical IP addresses. When a DNS query fails, it disrupts this process, leading to errors and inaccessible websites.
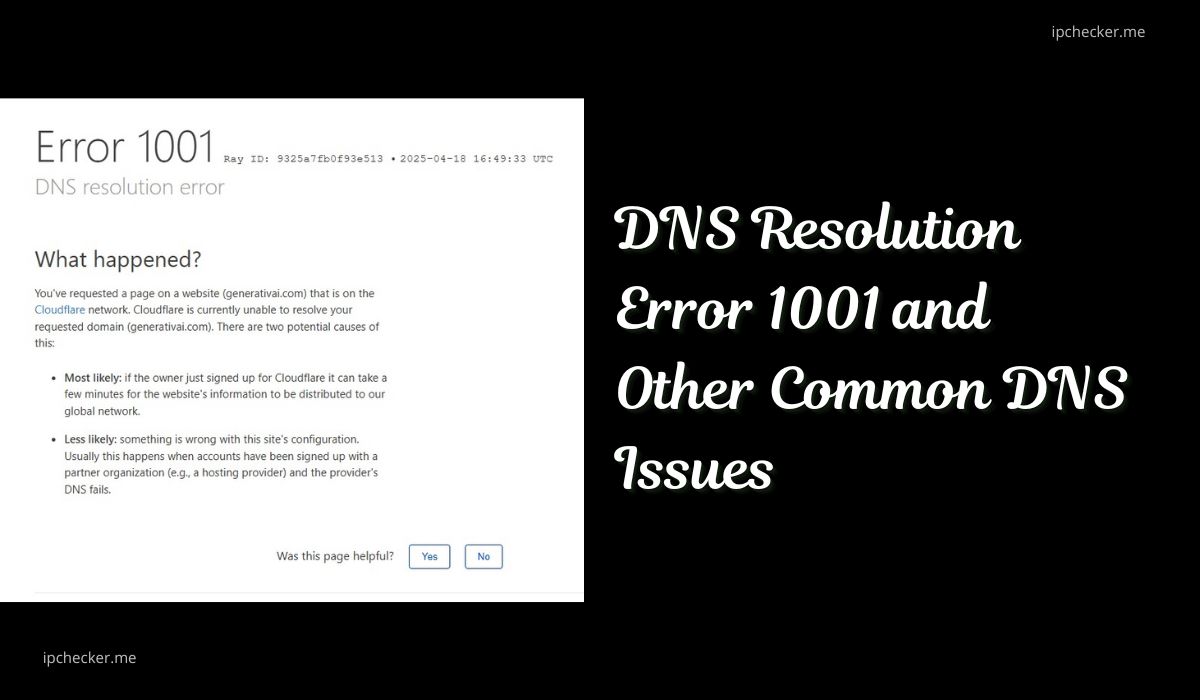
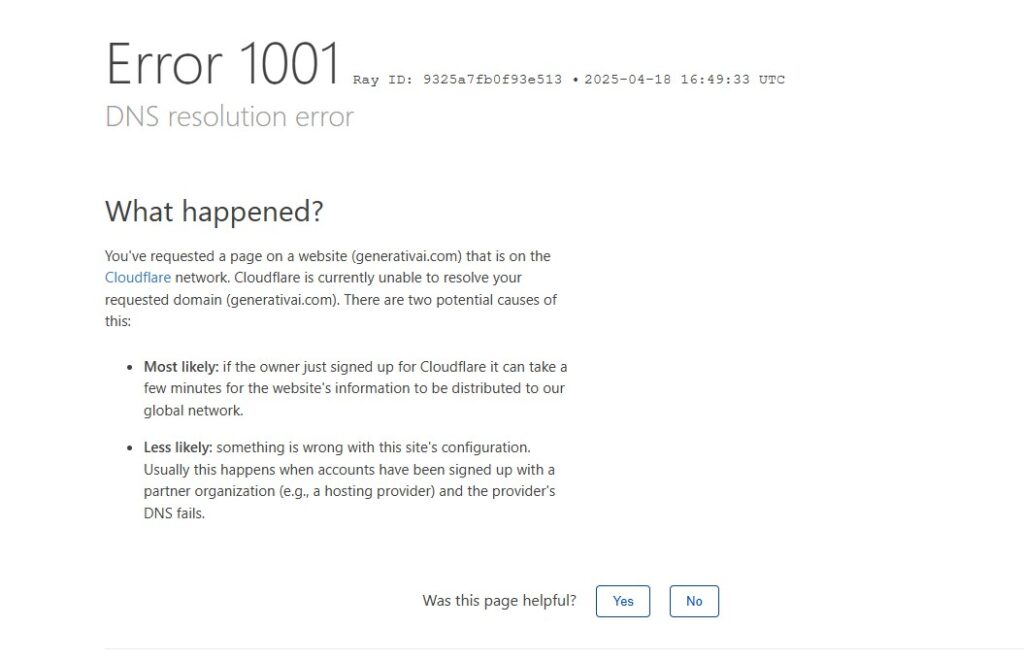
DNS Resolution Error 1001
What Is Error 1001?
Error 1001 indicates a DNS resolution failure, meaning the DNS server couldn’t translate the domain name into an IP address. This error is commonly associated with Cloudflare’s services.
Common Causes of DNS Resolution Error 1001
- Non-Existent Domain: A request is made to a Cloudflare IP for a domain not configured with Cloudflare.
- Improper CNAME Configuration: An external domain not using Cloudflare has a CNAME record pointing to a Cloudflare domain.
- Unresolved CNAME Target: The target of a CNAME record doesn’t resolve, possibly due to DNS propagation delays or misconfigurations.
- DNSSEC Issues: DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) is enabled at the registrar but not properly configured with Cloudflare, leading to resolution failures.
- Nameserver Mismatch: The domain’s nameservers no longer point to Cloudflare, causing DNS resolution to break.
- Always Online Feature: Cloudflare’s Always Online feature is enabled for a custom hostname, which can trigger Error 1001 if misconfigured.
Read also: Dangers of Using Free WiFi Near Me
How to Resolve DNS Resolution Error 1001
- Ensure the domain is correctly set up in Cloudflare’s dashboard.
- Confirm that CNAME records point to valid and resolvable targets.
- If DNSSEC is enabled at the registrar, disable it before adding the domain to Cloudflare, then re-enable it following Cloudflare’s guidelines.
- Ensure the domain’s nameservers are correctly pointing to Cloudflare’s nameservers.
- Disable the Always Online feature for custom hostnames if it’s causing issues.
Recommneded: What is a Virtual IP Address – Purpose and Benefits
Other Common DNS Errors
1. Error 1000: DNS Points to Prohibited IP
- Cause: An A record in Cloudflare’s DNS points to a Cloudflare IP address, leading to a loop.
- Solution: Update the A record to point to the correct origin server IP address.
2. Error 1002: DNS Points to Prohibited IP
- Cause: Similar to Error 1000, this occurs when a DNS record points to an IP address that Cloudflare prohibits.
- Solution: Correct the DNS record to point to an allowed IP address.
3. Error 1014: CNAME Cross-User Banned
- Cause: A CNAME record points to a domain in a different Cloudflare account, which is not permitted by default.
- Solution: Use Cloudflare’s SaaS offering to allow such configurations or restructure the DNS setup to comply with Cloudflare’s policies.
4. SERVFAIL
- Cause: The DNS server encountered an internal failure while processing the query, often due to misconfigurations or DNSSEC validation issues.
- Solution: Check DNS server logs, validate DNSSEC configurations, and ensure all DNS records are correctly set up.
5. REFUSED
- Cause: The DNS server refused to process the query, possibly due to access restrictions or misconfigured zone files.
- Solution: Review server access controls and zone file configurations to ensure proper permissions and settings.
Recommended: All DNS Record Types you Should Know
6. DNS_PROBE_FINISHED_NXDOMAIN
- Cause: The domain does not exist in the DNS, often due to typos or missing DNS records.
- Solution: Verify the domain name for accuracy and ensure that the necessary DNS records are present and correctly configured.
How to Troubleshooting DNS Errors
- Use Diagnostic Tools: Tools like
dig,nslookup, and online DNS checkers can help identify DNS issues. - Check DNS Records: Ensure all necessary DNS records (A, AAAA, CNAME, MX, etc.) are correctly configured.
- Review DNSSEC Settings: If DNSSEC is enabled, confirm that it’s properly set up with valid signatures and keys.
- Verify Nameserver Settings: Ensure that the domain’s nameservers are pointing to the correct DNS provider.
- Clear DNS Cache: Flush local DNS caches to eliminate outdated or corrupted entries.
- Monitor DNS Propagation: Be aware that DNS changes can take up to 48 hours to propagate globally.
How to Preventing DNS Issues
- Periodically review DNS configurations to catch and correct errors early.
- Use monitoring tools to detect DNS issues promptly.
- Ensure that those managing DNS settings understand best practices and common pitfalls.
- Choose reputable DNS providers that offer robust support and infrastructure.